Current state of Indian higher education landscape:
Globalization in education means breaking down the barriers and connecting with universities world-wide. Making universities in every country visible to each other, facilitating knowledge flows, values on global learning, and creation of new opportunities for advanced graduates. India has been recently, witnessing a growth in alliances with a number of foreign varsities
India’s higher education system is the third largest in the world, next to the United States and China.
Around 37.4Mn. students are enrolled in Higher education in India with a GER of 26.3% in the age group of 18–23. Govt. aims to increase it to 50% by 2035 under NEP’20
The expansion and reform of the higher education system in India is driven by Central agencies. State Govt. has been empowered to grant permission for establishment of private universities. All universities need to be approved by UGC and get accreditation from NAAC.
The decentralisation of power has to led increase in number of private universities in India. Various state governments have encouraged and justified this growth in order to increase enrolment in higher education, and private capital has welcomed this state encouragement. India, currently has 51k+ institutions which comprises of Universities, Colleges, Stand-alone institutions and deemed to be university.
However, there quality of these private universities is long debated. This is also evident from the lower enrollment ratio in private colleges as compared to govt. colleges
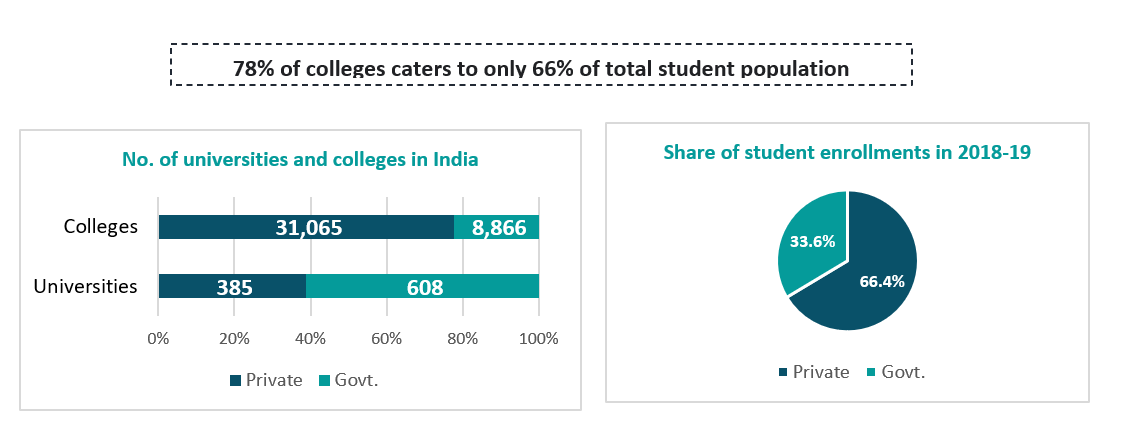
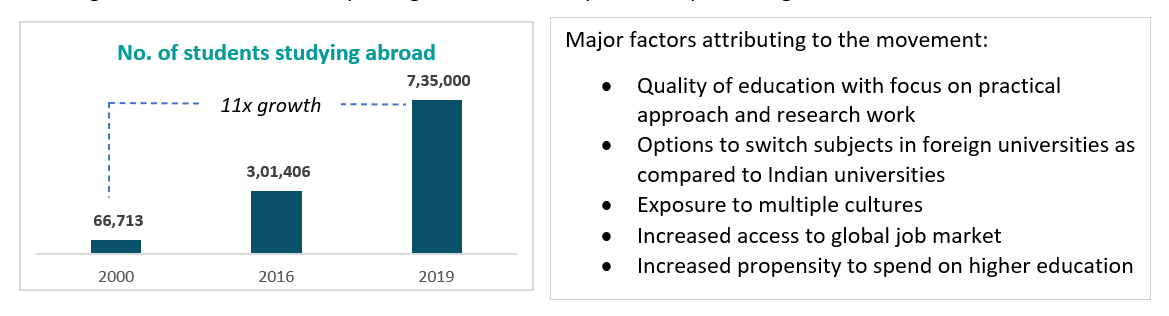
There is a rising demand for International colleges among Indian students:
India has witnessed a growing demand for international degrees with more students moving abroad for higher education. There is a paradigm shift in the way students pursue higher education
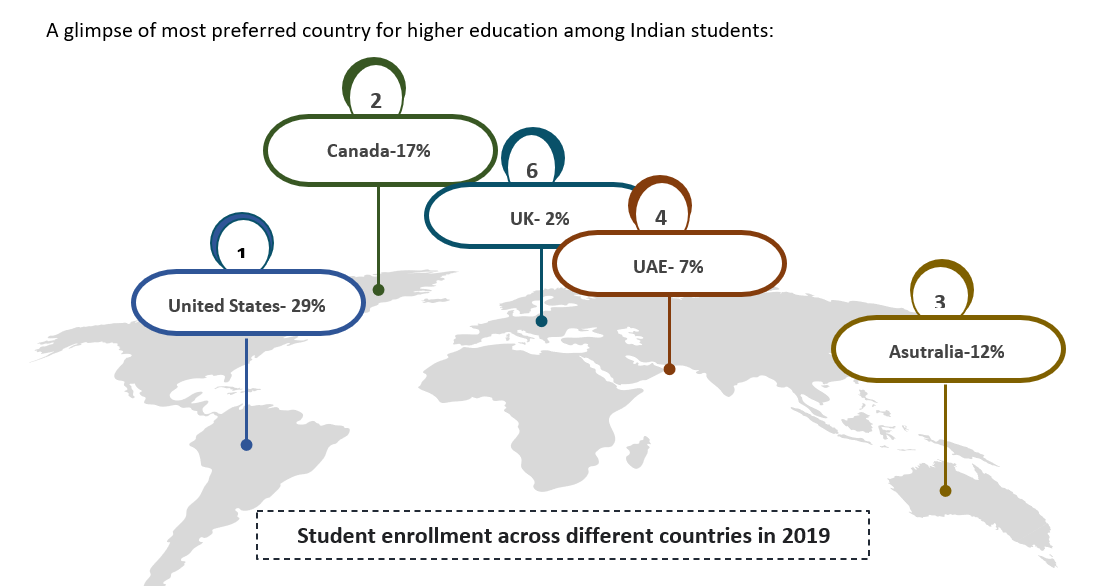
A glimpse of most preferred country for higher education among Indian students:
Domestic universities are trying to capitalize the growing trend and have started partnerships with many foreign universities. Indian universities benefit from:
- Improved academic offering and curriculum development
- Increased credibility of Indian university brand among students
- Enhancement in pedagogical skills for the Indian teaching community. Training and certification in international courses
Global partnerships are helping internationalisation of Indian higher education system:
Partnership between domestic and foreign university is guided by UGC regulations and foreign university bill. Though, these policies are democratised, yet Indian universities have been collaborating with foreign varsities in various ways under the restrictive regulations
Popular collaboration ideas are:
A. Foreign universities have also set-up campuses in India in partnership with existing schools as per the current Govt. regulations. Degree is awarded by Indian institute. American institutes have set-up the highest number of collaborative programs with domestic universities. Example of other such collaborations are:

B. Domestic universities are constantly adopting the international methods of collaboration, creating a pathway for foreign universities to enter Indian education system.

Examples of Short duration programs: IITs and IIMs have been engaging with foreign universities from decades now through various forms of partnerships like- student exchange programs, faculty exchange and collaborative research and development programs.
Long duration programs:
- O.P Jindal university has developed dual degree program with Deakin university Australia where 2-year program is conducted in India and the remaining 2 year in Australia. Two degrees are awarded- one from each of the university
- Australia’s Monash University centre on the campus of the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay in Mumbai, which issues joint degrees with IIT-B
- Amity university provides articulation program. Students can study the courses of the first few years at the Indian institution, with the International institution recognizing the credits. Degree is awarded by foreign university
C. Pathways program: Pathway programs has been in existence from long and used by foreign universities to attract international students. In India, many pathway program providers have emerged given the student’s increasing demand for foreign university education
Important characteristics:
- Online, offline or blended learning approach
- 10–11 months study in India in presence of foreign university faculty. Foreign university to provide 1 year exemption in their degree course when students pursue remaining under-graduate degree in foreign university
- Credits earned while studying in India transferred to foreign university
- At the end of the degree program, foreign university to award degree to student
Pathway program providers are fragmented in India with small players. Domestic universities directly partner with foreign university hence the need for pathways is not seen. Some examples are: Abroad Unified pathway programs, Overseas Unified pathway programs, IDP among others
Govt. is also supportive of global partnerships with introduction of new laws:
Indian regulations w.r.t foreign varsities is opening-up giving way for increased autonomy for institutions that will change the landscape for partnerships and exchanges with foreign institutions
- NEP 2020 is making way for large-scale transformational reforms including restructuring the higher education system into three categories of degree-awarding institutions, greater institutional autonomy, a new National Research Foundation and renewed commitment to allow foreign universities into India as part of an internationalisation drive. NEP’20 proposes to allows top 100 global universities to set-up their establishment in India
- Draft UGC regulation’21 proposes to allow twinning arrangements, Joint degree programs among others
- MOOC has seen an overhaul. UGC new regulation in 2020 has increased the number of credits that can be earned online to 40% for higher education
Moment of economic liberalisation for higher education system:
International partnerships between universities are beneficial to all, from the staff and students to the world as a whole. Govt. policies will encourage set-up of foreign universities in India, promote joint degrees. The rate of internationalization will grow rapidly now, with unhindered communication channels and inexpensive travel. Universities across the world are already seeking to make the most of the possibilities this presents by forming global partnerships and fostering relationships with Indian institutions
Watch this space for more on Education, EdTech and everything in between



